Prior research provided evidence of failed EMR implementations due to resistance on the part of physicians, nurses, and clinical administrators. Only 25% of office-based physicians had basic EMR systems and only 10% have fully functional systems. Resistance to using EMR systems puts both hospitals and patients at greater risk of possible medical mishaps.
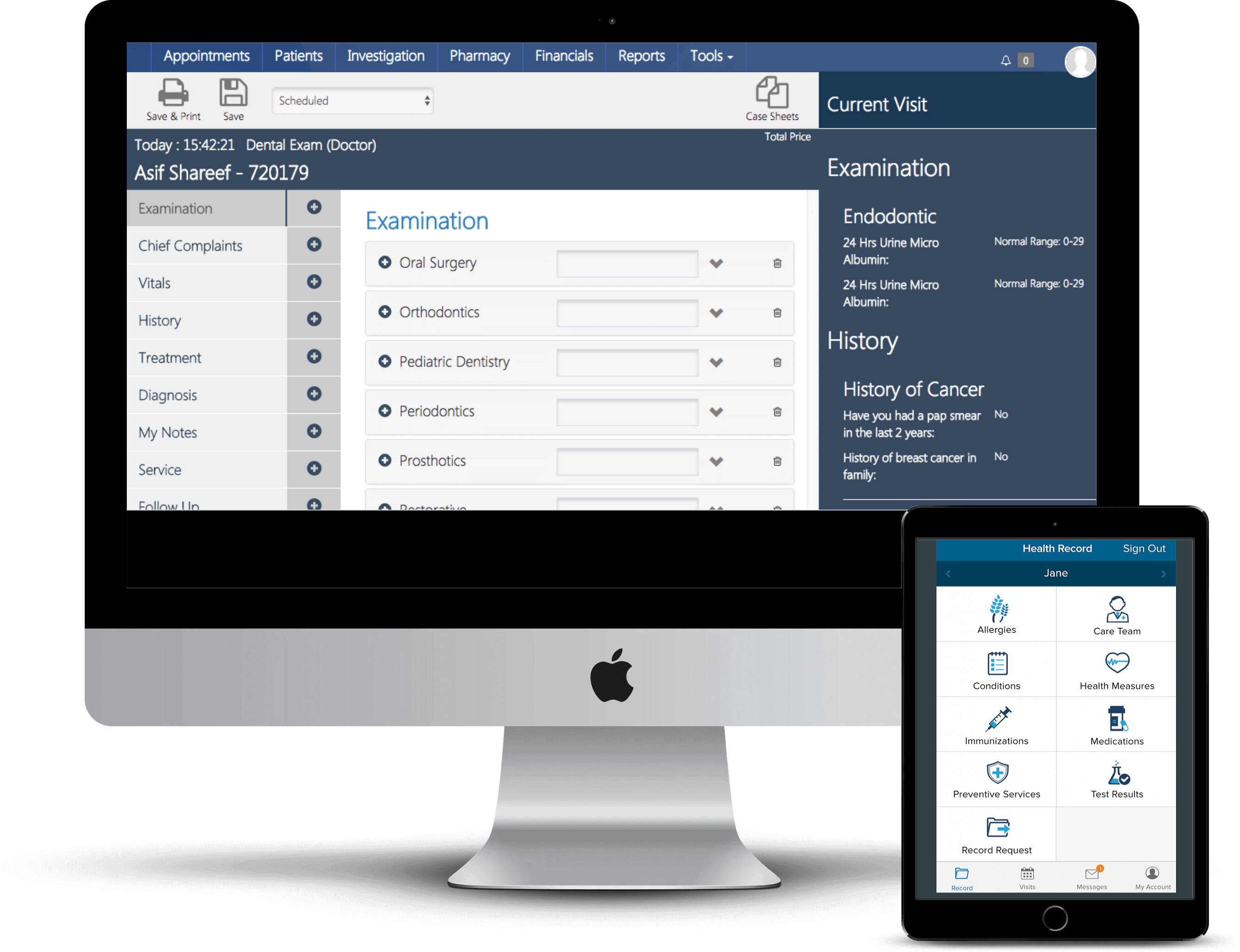
This is a quantitative method study that measured the relationships between six constructs, namely computer self-efficacy (CSE), perceived complexity (PC), attitude toward EMR (ATE), peer pressure (PP), anxiety (AXY), and resistance to use of technology (RES).
The study also measured four covariates: age, role in healthcare, years in healthcare, gender, and years of computer use. The study used Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) and an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) to address the research hypotheses proposed.
A Web-based survey instrument consisting of 45 items was used to assess the six constructs and demographics data. The data was collected from 350 healthcare professionals across the United States.
Construct validity and reliability was done using the Delphi method. A pilot study of 20 participants was conducted before the full data collection was done, resulting in some minor adjustments to the instrument. The analysis consisted of SEM using the R software and programming language.
Lack of a formal training program has been implicated as a reason for resistance to the use of computer systems in the work environment in a 1998 study by Jayasuriya. Although this was not taken into consideration in this research but was suggest by the chair for future work. Overcoming healthcare professional’s resistance to the implementation of EMR systems can often require diplomacy and persuasion, rather than mandates and requirements.
To empirically assess the contributions of the independent variables of CSE, PC, ATE, PP, and AXY on the dependent variable of healthcare professionals’ resistance to EMR systems, while controlling for the demographic indicators of physicians’ age, gender, precise healthcare role and years in the profession.
Very few studies empirically investigated the impact of CSE, PC, ATE, PP and AXY on the resistance to use EMR systems. The literature concluded that the addition of additional constructs could server as s better predictor to the Resistance to EMR systems.
To examine hypotheses 1 through 5, the paths from CSE, PC, ATE, PP, and Anxiety to medical professionals’ resistance to using EMR systems was examined. Each of the variables are latent variables within the model. The standardized regression weights were interpreted to examine the strength of the relationship between CSE, PC, ATE, PP, and Anxiety to medical professionals’ resistance to using EMR systems.
The aim of this study was to determine if CSE, PC, ATE, AXY and PP have significant effect on RES.
Emmanuel Bazile All Rights Reserved
With 25 years of experience in healthcare IT implementation, Emmanuel began his career at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, working as an assistant manager for a billing system implementation. Over the years, he has explored various aspects of the healthcare IT domain, successfully implementing several laboratory information systems and electronic medical record (EMR) systems, such as Cerner Millennium and Epic EMR.
In 2005, Emmanuel shifted his focus to public health, working on bio-surveillance implementation for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). He contributed to the BioSense Data Provisioning Project and performed extensive analysis of HL7 messages in hospitals and healthcare facilities. Additionally, Emmanuel requirements analysis for the CDC BioSense Analysis, Visualization and Reporting (AVR) project and played a key role in publishing the Situational Awareness updates to the BioSense System Requirements Specification (SRS).
Over the past 11 years, Emmanuel has worked in the Middle East, implementing the Epic EMR system at Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi. As a multidisciplinary team member, he has taken on various roles, including SCRUM Master, Project Manager, Integration Engineer, and Platform Engineer. Concurrently working as an adjunct university faculty member, teaching graduate-level courses in Systems Life Cycle and undergraduate courses in Health Information Systems
From a technological standpoint, Emmanuel has designed, installed, and implemented complete hospital integration systems using Rhapsody Integration Engine, MS SQL Server, and Public Health Information Networks Messaging System (PHINMS). He has also developed over 10,000 interfaces some of which coded in Java and JavaScript.
In 2019, Emmanuel expanded his skill set and entered the field of digital marketing, quickly becoming a proficient Digital Marketing Strategist. He has since helped numerous clients develop robust digital marketing strategies for their businesses. His expertise encompasses Social Media Marketing, On-page and Off-page SEO, Google Ads, and Google Analytics. Additionally, he and a team have managed clients’ website development projects, ensuring that each site is optimized for SEO, further enhancing their online presence and performance.
Alongside their digital marketing expertise, Emmanuel has delved into the world of Affiliate Marketing, where Emmanuel and his team successfully managed and executed campaigns for a variety of clients. By identifying the right products and services to promote, Emmanuel and his team helped clients generate passive income streams and increase their overall revenue.
Their approach to Affiliate Marketing involves creating valuable content that educates and engages the target audience, while strategically incorporating affiliate links. Emmanuel and his team have experience working with multiple affiliate networks and platforms, ensuring optimal tracking and reporting of performance metrics. By staying up to date with the latest trends and best practices, Emmanuel and his team have been able to optimize affiliate campaigns for maximum results, fostering long-term partnerships and sustainable growth for their clients.
As an accomplished professional, Emmanuel holds dual Bachelor of Arts degrees in Linguistics and English, a Master of Science in Health Information Systems from the University of Pittsburgh, and a Ph.D. in Information Systems from Nova Southeastern University.
Professor Bazile is a dedicated technology instructor and Adjunct Faculty professor, who began his teaching career in April 2000 at the Business Career Institute in Las Vegas, Nevada.
In 2001, he expanded his expertise by training nurses in the use of Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems. His experience in both technology and healthcare led to his appointment as an Adjunct Faculty professor at the University of Phoenix in May 2008, where he has taught several graduate-level information technology and healthcare information systems courses.
Dr. Bazile has also developed an HL7 course, which he has taught at various healthcare facilities, drawing from his own book, “HL7: Introductory and Advanced Concepts,” currently available on Amazon. With a passion for teaching and a commitment to ensuring students get the most out of each course he teaches, Dr. Bazile is a valuable asset to both his students and the institutions he serves.

My teaching philosophy as an Information Systems professor in healthcare is built on the concept that education should equip students to be confident and capable problem solvers who are prepared to traverse the complicated and ever-changing landscape of Healthcare IT.
In order to accomplish this, I prioritize the creation of a dynamic and engaging learning environment that encourages students to engage with course material and with one another. This involves employing a range of teaching approaches, such as lectures, seminars, and hands-on activities, to ensure that students learn in the manner that best matches their learning style.
I believe the reason we have Information Systems as a discipline is to allow students to apply technology to solve real world problems. If that is the case, both undergraduate and graduate students have to be challenged to incorporate their core academic courses with their matriculated subjects. As such, it is important that students enter their Junior and Senior years with a strong command of the core courses such as Programming, databases, networks, hardware and software, as they serve as the foundation upon which real-world solutions will be built.
I also believe in the importance of incorporating real-world examples and case studies into my courses, as this helps to connect abstract concepts to practical applications. Additionally, I encourage students to apply what they are learning to their own personal and professional goals, as this helps to make the material more meaningful and relevant to their lives.
I strive to foster a positive and supportive learning environment where all students feel comfortable asking questions and participating in class discussions. I believe that this is key to fostering a sense of community and ensuring that all students have the opportunity to succeed.
I have also taught online courses. I have found in an asynchronous learning environment it can be difficult to apply the Peer Teaching or Experiential Learning Pedagogical Approaches. However, I have found the Discovery Learning approach to works quite well. Along with a boost to students’ self-confidence, Discovery Learning in an online environment allows students to synthesize information, expand on existing concepts on their own, while experiencing a positive outcome through trial and error.
Ultimately, my mission as an educator, and a Healthcare IT Information Systems professor is to provide students with the knowledge, skills, and confidence they need to thrive and succeed in their careers and to be technological leaders. By creating a positive and supportive learning environment, incorporating real-world examples and case studies, and encouraging students to apply what they are learning to their own objectives; my hope is to inspire and empower all students to achieve their full potential.
A total of 310 responses were originally received. Any response containing missing data due to unclicked radio buttons or unchecked checkboxes were first reviewed, and, if justified, were omitted from analysis. For surveys with missing data, a total of 18 responses were removed. In order to address any issues with response-set, the data was downloaded into Microsoft Access and queries ran to identify responses that contained the same values for each question. A total of 16 responses were found to be qualified for removal. Another 18 were identified as outliers and removed leaving a total of 258 responses for the study analysis.
In order to assess multivariate outliers, the Mahalanobis distances were calculated and plotted against their corresponding Chi-Square distribution percentiles (Schmidt & Hunter, 2003). The resulting scatterplot is similar to a univariate normal Q-Q plot, where deviations from a straight line show evidence of non-normality. The data showed indications of moderate deviations from multivariate normality, as indicated by the concavity of the data points. There were no additional multivariate outliers or missing values in the data after the removal of 52 responses.
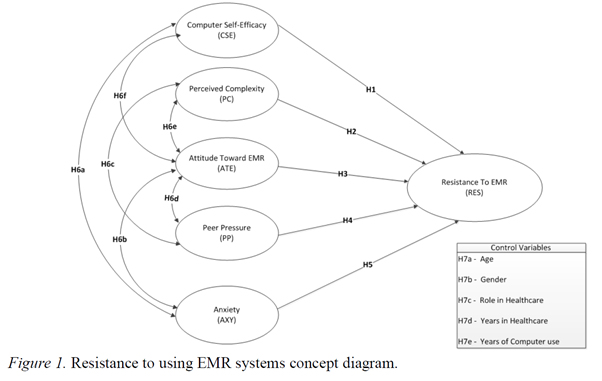
Frequencies and percentages were conducted for the demographics indicators, while means and standard deviations were calculated for the continuous indicators. For gender, there were 151 females (59%) and 107 males (41%) in the sample. For ethnicity, most participants were Caucasian (119, 46%), followed by African American (56, 22%). The two most populous education levels were Bachelor’s (90, 35%) and Master’s (62, 22%). The biggest proportion of the sample by age group was the 35-44 age group (101, 39%) followed by the 45-54 age group (59, 23%).
Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Composite Reliability
A CFA was conducted along with a reliability analysis to assess construct validity. Examination of modification indices and factor loadings indicated that CSE1, CSE5, CSE7, PC5, ATE1, ATE6, ATE8, PP5, and PP6 were all causing significant problems with the model parameters. The results of the last iteration of the CFA performed in R showed significantly improved fit, although still poor overall (χ2(545) = 2125.61, p < .001, CFI = 0.82, TLI = 0.81, RMSEA = 0.11). The high degrees of freedom indicate that a very large number of parameters are being estimated in this model.
Composite Reliability
For the full model, each construct had excellent reliability. The ATE latent construct had a composite reliability value of 0.89. The ORC construct had a composite reliability value of 0.94. The CSE latent construct had a composite reliability value of 0.85 and PC had a composite reliability value of 0.95. For PP and RES, the composite reliability scores were 0.80 and 0.96 respectively. These values indicate that the loadings for each construct were all directionally similar, and that the items in each construct show a high degree of consistency.
Cronbach’s Alpha
Cronbach’s alpha values were calculated for the items in each construct. The alphas for PC (α = 0.90), AXY (α = 0.94), and RES (α = 0.94) indicated excellent reliability. The alphas for CSE (α = 0.80), ATE (α = 0.88), and PP (α = 0.83) all showed good reliability. These values confirm the results of the composite reliability tests, and reiterate the high degree of reliability within each latent construct.
Partial Least Squares – Structural Equation Modeling
A partial least squares- structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) was conducted to determine how well the data fit the proposed model, and discern whether significant relationships existed between the independent and dependent constructs. The full model showed AVE values of 0.53 for ATE, 0.69 for AXY, 0.44 for CSE, .72 for PC, .35 for PP, and 0.81 for RES. The high values for AXY, PC, and RES indicate that the amount of variance accounted for in the manifest variables is sufficiently high. The values for ATE, CSE, and PP indicate that some of the variance in the manifest variables is left unexplained.
Structural Model
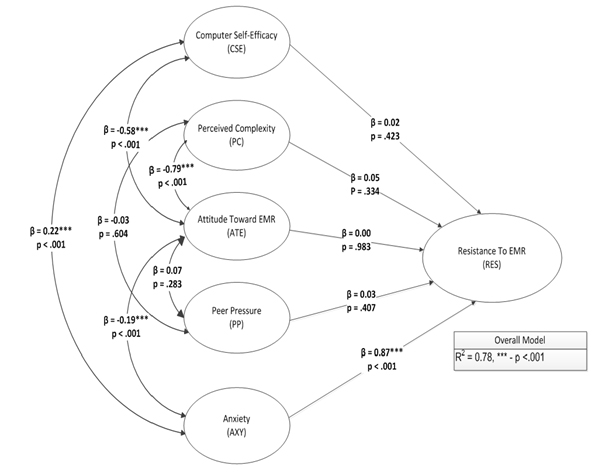
Once the measurement model had been tested for model specification, the structural model was tested to determine if ATE, AXY, CSE, PC, and PP had a significant effect on RES. A path weighted model was calculated using 10,000 bootstrap samples in R. The results showed a pseudo R-squared value of 0.78. This indicates that approximately 78% of the variance in RES is explainable by the collective effects of CSE, PC, ATE, PP, and AXY.
Further examination of the effects indicated that AXY had a highly significant effect on RES (B = 0.87, p < .001). This indicates that a standard deviation increase in AXY increases the expected value of RES by 0.87 standard deviations. CSE did not have a significant effect on RES (B = 0.02, p = .423). Additionally, CSE (B = 0.02, p = .423), PC (B = 0.05, p = .334), ATE (B = 0.00, p = .983), and PP (B = 0.03, p = .407) did not have significant effects on RES. Table 11 outlines the results of the path estimates.
Correlation Analyses
Both Pearson and Spearman correlations were calculated on the composite scores. The results of the Pearson correlations indicated that CSE was significantly correlated AXY (r = 0.22, p < .001) and RES (r = 0.21, p < .001). The results also indicated that PC was significantly correlated with ATE (r = -0.79, p < .001), AXY (r = 0.18, p < .001), and RES (r = 0.20, p < .001). ATE was significantly correlated with AXY (r = -0.19, p < .001) and RES (r = -0.19, p < .001). AXY was significantly correlated with RES (r = 0.85, p < .001).
ANCOVA Analyses
An analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was conducted to determine if a significant relationship existed between the AXY, PP, CSE, PC, ATE scores and RES controlling for Gender, Age, Ethnicity, Education, and Specialty. The overall model was found to be significant (F(63,194) = 53.39, p < .001), with an R2 value of .95, indicating that 95% of the variance in RES was explained by the collective effect of the independent variables and covariates.
Since the overall model was found to be significant, the model’s covariates were assessed. The AXY (F(10,194) = 262.20, p < .001), ATE (F(7,194) = 2.20, p = .036), Years computers (F(1,194) = 5.71, p = .018), and PC (F(12,194) = 2.00, p = .026) scores were found to be significant, indicating that a significant amount of variance in RES is explained by AXY, ATE, and PC.
A path diagram depicting the results of the structural model.
This research investigated Computer Self-Efficacy (CSE), Perceived Complexity (PC), Attitudes toward EMR Systems (ATE), Peer Pressure (PP), and Anxiety (AXY) to determine whether these constructs as individuals, or as a group, or coupled together with some other factors could significantly explain resistance to EMR systems. Quantitative examination of self-reported survey results was performed to understand the strength and significance of the relationships, while these relationships were investigated to test the strength of model fit.
the regression paths of the structural model were examined to test the hypotheses. Significance was determined using an alpha level of .05. The model had an overall R2 value of 0.78. This indicates that approximately 78% of the variability in RES can be accounted for by CSE, PC, ATE, PP, and AXY. Since the overall model was significant, the individual coefficients can be interpreted. Some of the hypotheses were supported by the results of this study, and some were rejected. The construction of a data model of the relationships in this study could not meet thresholds that would be evidence of a good fit of the relationships identified in the study.
The fifth hypotheses tested the influence of AXY on resistance to EMR systems. AXY was expressed to be significantly related to resistance (r=.87, p<.001). This finding supports the hypothesis that anxiety with the EMR system will lead to medical care professionals rejecting use of the system. Unlike the findings of the first four hypotheses, the findings of the current study support previous research. Angst and Agarwal (2009) indicated that AXY is a factor which is significantly related to the problem of EMR system resistance. Based on the empirical findings of previous research, the present research and conceptual propositions and conclusions in previously written scholarly articles, there is a great deal of support for the finding that AXY is significantly influenced by EMR resistance.
The findings of this research do not support all findings by previous researchers, and there are multiple relationships which had been established as being significant that were identified as being insignificant in the current research. Generally, because of the inconsistency of previous findings and the current study there may be elements related to the sample examined or other contextual factors which may contribute to the inconsistency that exists. Ultimately, it is suggested that there be further research done on the problem of resistance to EMR system use.
Ultimately the findings support a new take on the problem of EMR system resistance that may contribute to the ways in which scholars investigate the problem of EMR resistance in general. This may also help with the way practitioners approach EMR systems, and articulate value of the systems to medical professionals investing record-keeping systems in the workplace.